Class 02
Class 02
Working with Circuits
A closed loop through which current can flow is an electric circuit.
A voltage source, such as a battery, conductor, typically wire, is required for every electric circuit. They could also have one or more electric devices.
A circuit diagram, which employs standardized symbols to represent the circuit's components, can represent an electric circuit.
Ohm’s Law
V= Voltage (Volt) , voltage is an electric potential difference. Similar to the gravitational potential difference between the top and bottom of a hill
I = Current (Amp), current is the flow of electrons (electricity) in an electronic circuit, whereas voltage is the amount of force pushing the flowing electrons.
R = Resistance (Ohm); resistance is a measure of a circuit's opposition to the flow of electric current. Additionally, resistance is a measure of how a substance or equipment restricts the flow of electricity through it in an electrical sense.
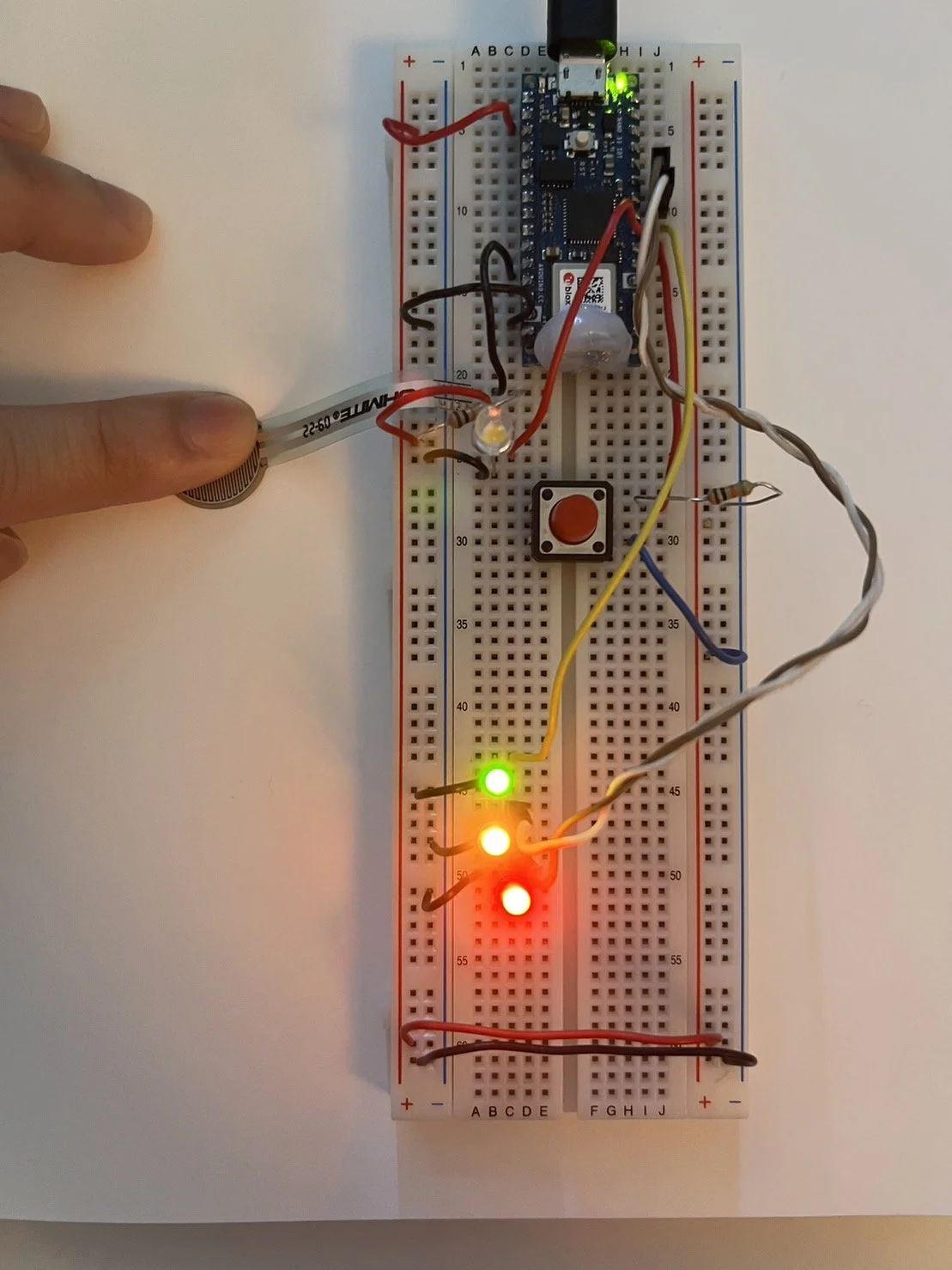
Create the circuit
LED
Variable Resistor
Notes
LED GREEN
if(Touch > 200){ digitalWrite(5, HIGH);}
LED YELLOW
if(Touch > 500){ digitalWrite(6, HIGH);
LED RED
if(Touch > 800){ digitalWrite(7, HIGH);
Lab digital input and output
Code
Reading : THE PSYCHOPATHOLOGY OF EVERYDAY THINGS
Discoverability and understanding are two of a good design's most important characteristics.
Discoverability: Is it even possible to determine which activities are accessible and how they are executed?
What does it all imply, exactly? How should the product be utilized? What do all of the different settings and controls mean?
Industrial designers emphasize form and material
Interactive designers emphasize understandability and usability
Experience designers emphasizing the emotional impact